Transumbilical laparoscopic-assisted appendectomy versus laparoscopic appendectomy in children: a single center experience
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Accepted: 19 March 2023
Authors
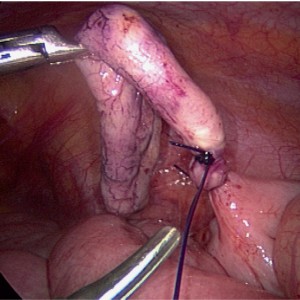
Laparoscopic Appendectomy (LPSA) is the first choice for appendectomy in pediatric surgery. Trans-Umbilical Laparoscopic Assisted Appendicectomy (TULAA) is another used technique. We compared both these procedures used for the treatment of acute appendicitis. The study was conducted between January 2019 to December 2020. Patients were divided into two groups: LPSA and TULAA groups. The collected data were: operative time, number of conversions, time of canalization and hospital stay. A total of 181 patients were included: 73 were kept in the LPSA and 108 in the TULAA group. Mean operative time was 70.9 minutes (range 45-130 min) for LPS and 56.4 (30-145 min) for TULAA group (p <0.0001). Complications rate showed no statistically significant difference between both the two groups. However, conversions showed a statistically significant difference (p=0.04). Both techniques showed similar results. TULAA technique takes a significantly shorter operating time. The selection between LPSA and TULAA techniques depends on the experience of the surgeon’s work and the personal laparoscopic learning curve. In our experience LPSA was a useful technique to improve the laparoscopic skill of the pediatric surgery residents.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






